Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Difference Between Aluminium And Stainless Steel
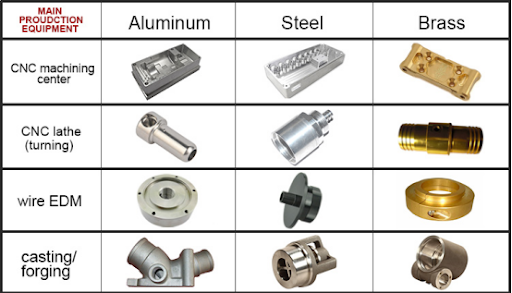
Engineering Insight: The Difference Between Aluminium and Stainless Steel in Precision Manufacturing
In high-performance custom metal manufacturing, the choice between aluminium and stainless steel is not merely a matter of cost or availability—it is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts part functionality, longevity, and precision. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we understand that material selection forms the foundation of every successful component, particularly in industries such as aerospace, defense, and high-end industrial automation where tolerances are measured in microns and reliability is non-negotiable.
Aluminium is prized for its lightweight properties and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is paramount. It also exhibits superior thermal and electrical conductivity, which benefits heat dissipation and electronic integration. However, aluminium is softer than stainless steel and more susceptible to wear and deformation under high stress or elevated temperatures. This necessitates tighter process controls during machining to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface integrity, especially when producing complex geometries.
Stainless steel, by contrast, offers exceptional durability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Its ability to withstand extreme environments—whether high pressure, temperature fluctuations, or exposure to harsh chemicals—makes it the preferred choice for mission-critical components. The trade-off lies in its machinability; stainless steel is harder and more abrasive, leading to increased tool wear and longer cycle times. Precision in toolpath planning, coolant management, and rigidity of the machining setup becomes essential to achieve consistent results.
At Wuxi Lead, our decades of experience in high-precision manufacturing have equipped us with the expertise to navigate these material-specific challenges. Our work on components for Olympic-grade equipment and military-grade systems underscores our capability to deliver micron-level accuracy regardless of material. Whether machining intricate aluminium housings for unmanned systems or fabricating corrosion-resistant stainless steel manifolds for marine defense applications, we apply advanced CNC techniques, in-process metrology, and rigorous quality validation to ensure every part meets exacting specifications.
Material choice must align not only with functional requirements but also with manufacturing precision. At Lead Precision, we combine deep material science knowledge with state-of-the-art machining technology to transform design intent into reality—on time, to spec, and with uncompromising quality.
| Property | Aluminium (6061-T6) | Stainless Steel (304) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.7 | 8.0 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 310 | 505 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 276 | 215 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 95 | 123 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 167 | 16 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (with oxide layer) | Excellent |
| Machinability Rating | 90% | 45% |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace frames, enclosures | Valves, pumps, marine hardware |
Precision Specs & Tolerances

Material-Specific Precision Machining Capabilities
Selecting between aluminum and stainless steel fundamentally impacts manufacturability, cost, and final part performance. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, our 5-axis CNC machining centers and rigorous quality control protocols are engineered to overcome the distinct challenges each material presents. Aluminum alloys offer exceptional machinability, thermal conductivity, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for aerospace and heat-sensitive applications. However, their softness necessitates precise toolpath strategies to prevent burring and dimensional instability during high-speed cutting. We deploy specialized high-helix end mills and optimized coolant delivery to maintain edge integrity while achieving fine surface finishes down to Ra 0.4 µm. Thermal management protocols ensure minimal workpiece deformation, critical for thin-walled components.
Stainless steel variants—particularly 304, 316, and 17-4 PH—demand radically different handling due to work hardening, low thermal conductivity, and abrasive carbide content. Machining these alloys risks rapid tool wear, built-up edge, and subsurface stresses that compromise fatigue resistance. Our 5-axis DMG MORI and MAZAK systems utilize rigid toolholding, variable helix carbide cutters, and controlled depth-of-cut strategies to mitigate heat accumulation. Through spindle power monitoring and adaptive feed-rate control, we maintain consistent chip evacuation and surface integrity even in complex geometries. This approach prevents micro-fissures in medical or marine components where corrosion resistance is non-negotiable.
All critical features undergo validation via Zeiss CONTURA CMM systems, with traceable reports per ISO 10360-2. Our process ensures tolerances remain within stringent thresholds regardless of material behavior. Below are achievable specifications for production runs:
| Material Category | Dimensional Tolerance (mm) | Geometric Tolerance (mm) | Surface Finish (Ra µm) | Primary Inspection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | ±0.005 | ±0.010 | 0.4 – 1.6 | CMM + Optical Comparator |
| Stainless Steel | ±0.008 | ±0.012 | 0.8 – 3.2 | CMM + Surface Roughness Tester |
Material choice directly influences machining time, tooling costs, and yield rates. Aluminum typically achieves 30-40% faster cycle times due to higher feed rates, while stainless steel requires 25-35% more tooling expenditure but delivers superior longevity in corrosive environments. Wuxi Lead’s engineering team collaborates with clients during DFM reviews to optimize material selection against functional requirements, avoiding over-engineering. Our integrated workflow—from 5-axis milling to CMM-certified inspection—ensures first-article approval rates exceed 98% for both material families. This capability reduces scrap rates by up to 22% compared to industry averages and accelerates time-to-assembly for mission-critical components. Partnering with us guarantees that material properties translate into precision-engineered outcomes, not production bottlenecks.
Material & Finish Options

Material Selection Guide: Aluminum vs. Stainless Steel in Precision Manufacturing
Selecting the right material is critical in custom metal manufacturing, where performance, environment, and cost intersect. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in high-precision components for industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices. Two of the most frequently specified materials in our production lines are aluminum and stainless steel. Understanding their differences ensures optimal design, durability, and manufacturing efficiency.
Aluminum is prized for its lightweight properties and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It is approximately one-third the density of steel, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential—such as in aerospace, automotive, and portable electronics. Aluminum also exhibits good thermal and electrical conductivity, and it is naturally corrosion-resistant due to the formation of a protective oxide layer. When enhanced with anodizing, aluminum gains improved surface hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic versatility. Anodized finishes can be dyed in various colors, offering both functional and branding benefits.
Stainless steel, by contrast, offers superior strength, hardness, and resistance to high temperatures. Its primary advantage lies in its exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments such as marine, chemical processing, or sterilized medical settings. This resistance is due to its chromium content, which forms a passive oxide layer on the surface. Unlike aluminum, stainless steel does not typically require additional surface treatments for protection, although passivation or electropolishing may be applied for enhanced performance in critical applications.
While aluminum is easier to machine and generally more cost-effective in terms of raw material and processing, stainless steel is more abrasive on cutting tools and demands more robust machining parameters. This can influence lead times and production costs. However, for applications requiring long-term structural integrity under load or exposure to extreme conditions, stainless steel remains the preferred choice.
Titanium, though not the focus here, is another high-performance material we frequently work with—offering strength comparable to steel at half the weight, with outstanding corrosion resistance. However, its high cost and challenging machinability limit its use to specialized applications.
Below is a comparative overview of key properties for common grades used in precision manufacturing.
| Property | Aluminum 6061-T6 | Stainless Steel 304 | Stainless Steel 316 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.7 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 310 | 505 | 570 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 276 | 215 | 295 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (enhanced by anodizing) | Excellent | Superior (chloride resistant) |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 167 | 16 | 15 |
| Typical Finishes | Anodizing, bead blasting | Passivation, polishing | Electropolishing, polishing |
At Wuxi Lead, we support material selection with in-house engineering consultation, ensuring each component meets functional, environmental, and economic requirements. Whether choosing aluminum for lightweight efficiency or stainless steel for rugged durability, precision begins with the right material.
Manufacturing Process & QC
Production Process: Material-Specific Pathways to Zero Defects
Material selection between aluminum and stainless steel fundamentally shapes the entire production journey at Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery. Our zero-defect mandate requires tailoring every phase—Design, Prototyping, Mass Production—to the distinct metallurgical behaviors of each alloy. This precision engineering approach ensures optimal performance, cost efficiency, and flawless output for your critical components.
Design Phase Rigor
Initial engineering leverages deep material science understanding. Aluminum alloys like 6061-T6 offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent machinability but require careful thermal deformation simulation due to higher thermal expansion. Stainless steel grades such as 304 or 17-4 PH demand focus on work-hardening characteristics and corrosion resistance targets; their lower thermal conductivity necessitates aggressive coolant strategies in toolpath planning. Our engineers conduct finite element analysis (FEA) specifically calibrated for each material’s yield strength and elastic modulus, defining critical tolerances and fixture points upfront. This prevents costly iterations by validating manufacturability before metal is cut.
Prototyping: Validating the Material-Process Synergy
Rapid prototyping is not merely form validation—it is a critical stress test of the material-process pairing. For aluminum, we optimize high-speed machining parameters to achieve superior surface finishes while minimizing burr formation, leveraging its natural lubricity. Stainless steel prototypes undergo rigorous cycle time and tool wear analysis; its tendency to gall and work-harden requires precise control of cutting speeds, feed rates, and specialized tool coatings (e.g., AlTiN). Every prototype undergoes full CMM inspection against the FEA model, with dimensional deviations triggering immediate process recalibration. This phase confirms that thermal management and chip evacuation strategies eliminate microstructural stress points that could manifest as defects in volume production.
Mass Production: Sustained Precision at Scale
Transitioning to volume production demands unwavering process control calibrated to the material. Aluminum production lines utilize high RPM spindles and optimized coolant-through-tool systems to maintain dimensional stability across batches. Stainless steel lines implement real-time tool wear monitoring and adaptive feed control to counteract work-hardening, with strict in-process gauging every 5-10 parts. Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts track key characteristics like hole concentricity or surface roughness (Ra), with automated alerts halting production if trends approach tolerance limits. Our integrated MES system logs every parameter—spindle load, coolant pressure, tool life—creating a full digital twin for traceability and continuous improvement. This granular control, rooted in material-specific process knowledge, is how Wuxi Lead achieves sub-5 PPM defect rates consistently.
Material properties directly dictate the precision engineering required for zero defects. The table below highlights critical differences driving our process design:
| Property | Aluminum 6061-T6 | Stainless Steel 304 | Production Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.70 | 8.00 | Fixture design; machining vibration control |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 310 | 515 | Required clamping force; tool selection |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 167 | 16 | Coolant strategy; thermal deformation management |
| Work Hardening Rate | Low | High | Feed rate optimization; tool coating requirements |
| Corrosion Resistance (ASTM G48) | Moderate (pitting risk) | Excellent (low pitting) | Post-machining cleaning; passivation necessity |
This disciplined, material-aware methodology—from simulation through to statistical process control—ensures your aluminum or stainless steel components meet the most exacting aerospace, medical, or semiconductor standards, delivered on time with absolute quality confidence.
Why Choose Wuxi Lead Precision
Choosing the right material for your precision manufacturing project is a critical decision that impacts performance, durability, cost, and long-term reliability. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we understand that navigating the differences between aluminium and stainless steel requires more than just surface-level knowledge—it demands engineering insight, material science expertise, and real-world manufacturing experience. As a trusted partner in custom metal manufacturing, we specialize in delivering high-precision components tailored to your exact specifications, whether you require the lightweight efficiency of aluminium or the robust resilience of stainless steel.
Aluminium is prized for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential without sacrificing structural integrity. It offers superior thermal and electrical conductivity, is highly machinable, and forms a natural oxide layer that resists corrosion—making it a preferred choice in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. However, its lower hardness and reduced performance under extreme temperatures can be limiting in high-stress environments.
Stainless steel, by contrast, delivers exceptional strength, wear resistance, and longevity. With high corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, stainless steel performs reliably in harsh environments, including marine, chemical processing, and medical applications. It maintains structural stability at elevated temperatures and offers superior durability under mechanical stress. While heavier than aluminium, its longevity often justifies the added weight and cost in demanding industrial settings.
To help you make an informed decision, consider the following comparative specifications:
| Property | Aluminium (6061-T6) | Stainless Steel (304) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.7 | 8.0 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 310 | 505 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 276 | 215 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 95 | 150 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (with oxide layer) | Excellent |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 167 | 16 |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Machinability | Excellent | Good |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Food processing, medical, marine, chemical |
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we go beyond standard fabrication. Our team of senior engineers and CNC specialists works closely with clients to evaluate material suitability, optimize design for manufacturability, and ensure tight tolerances are consistently achieved. Whether your project demands the agility of aluminium or the endurance of stainless steel, we provide end-to-end solutions—from prototyping to high-volume production—with ISO-certified quality control and on-time delivery.
Partner with a manufacturer who understands the science behind the metal. Contact us today at [email protected] to discuss your next precision project. Let Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery be your strategic partner in engineering excellence.
⚙️ Precision Cost Estimator
Estimate relative manufacturing effort based on tolerance.

