Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Casting Vs Injection Molding
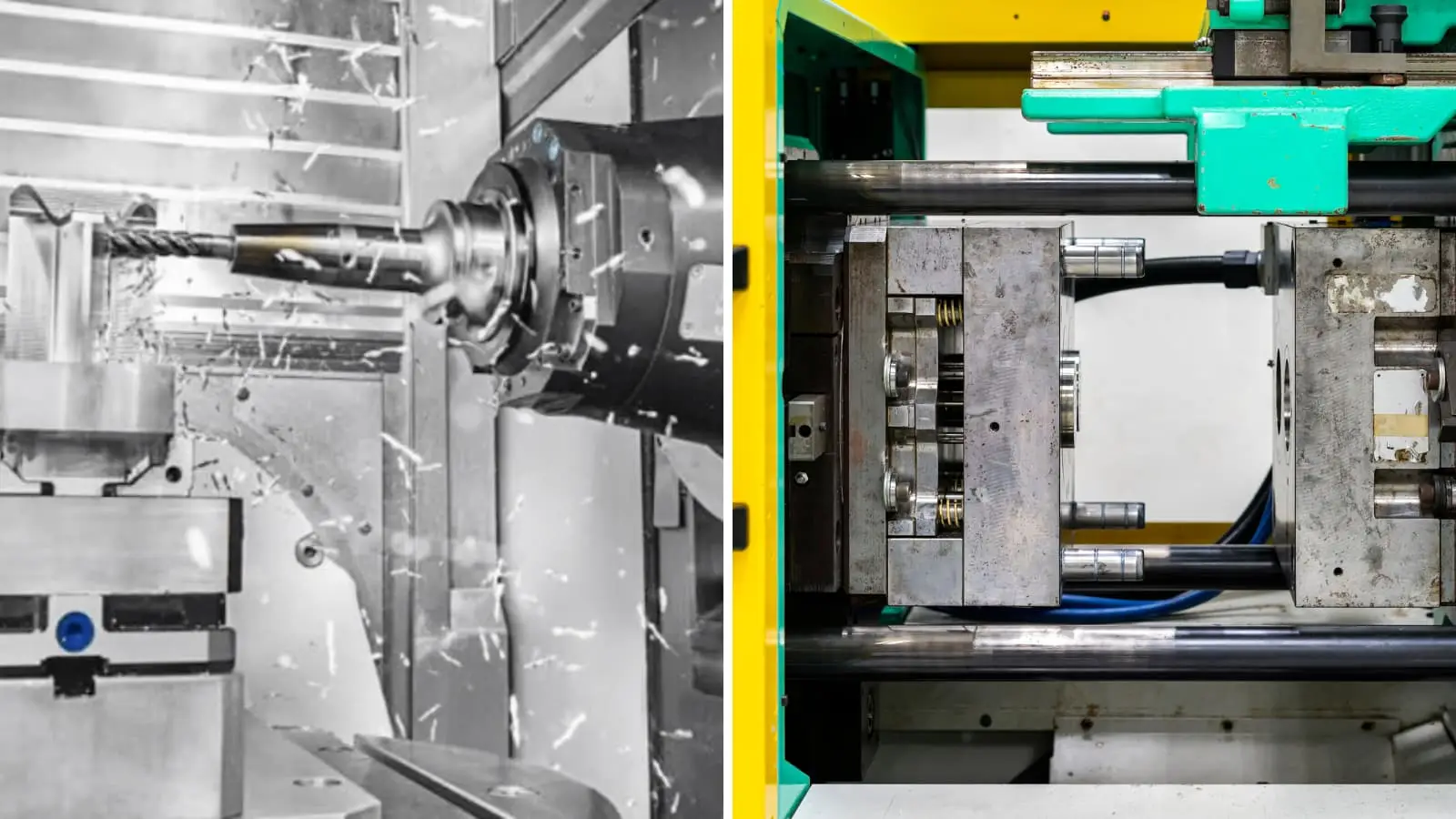

Engineering Insight: Casting vs Injection Molding – The Role of Precision in High-Performance Manufacturing
In the realm of custom metal manufacturing, the decision between casting and injection molding is not merely a matter of material or cost—it hinges on precision, repeatability, and long-term performance. Both processes serve critical roles across aerospace, defense, medical, and high-performance industrial sectors, yet their suitability depends heavily on the engineering demands of the final component. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we bring over 15 years of experience in delivering mission-critical components, including parts used in Olympic-grade equipment and military-grade systems, where tolerances are non-negotiable and failure is not an option.
Casting, particularly precision investment casting and die casting, excels in producing complex metal geometries from alloys such as aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. It is ideal for medium to large components requiring high thermal and mechanical resilience. However, dimensional accuracy in casting is influenced by shrinkage, mold integrity, and post-cast machining requirements. Without stringent process control, even minor deviations can cascade into functional failures—especially in load-bearing or high-speed applications.
Injection molding, while traditionally associated with plastics, also applies to metal injection molding (MIM) for small, intricate metal parts. MIM offers excellent surface finish and tight tolerances for high-volume production of miniature components, such as gears, connectors, and surgical tools. Yet, material limitations and the sintering process introduce challenges in achieving the mechanical strength required for extreme environments.
The defining factor in choosing between these methods is precision engineering. At Lead Precision, we integrate metrology-grade validation, finite element analysis (FEA), and real-time process monitoring to ensure every part meets exacting specifications. Our facility adheres to ISO 9001 and AS9100 standards, with in-house CNC finishing and non-destructive testing (NDT) capabilities to guarantee consistency across production runs.
Whether producing a titanium structural bracket for a defense platform or a corrosion-resistant manifold for Olympic aquatic systems, our approach centers on precision at every stage—from mold design to final inspection.
| Parameter | Die Casting | Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Investment Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Materials | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium | Stainless Steel, Tool Steel, Ti | Stainless Steel, Inconel, Ti |
| Tolerance Range | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | ±0.05 mm – ±0.1 mm | ±0.1 mm – ±0.2 mm |
| Part Size Range | 50 g – 10 kg | 0.1 g – 250 g | 10 g – 5 kg |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | 0.8 – 3.2 µm | 0.4 – 1.6 µm | 1.6 – 6.3 µm |
| Production Volume | Medium to High | High | Low to Medium |
| Secondary Machining | Often Required | Minimal | Frequently Required |
| Lead Time | 4–8 weeks | 6–10 weeks | 5–9 weeks |
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, our expertise in both casting and MIM enables us to guide clients toward the optimal process based on performance, volume, and precision requirements. With a proven track record in elite engineering applications, we ensure that precision is not an afterthought—it is the foundation.
Precision Specs & Tolerances
Technical Capabilities: Precision Engineering for Post-Casting and Post-Molding Operations
Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery specializes in advanced CNC machining for critical secondary operations following casting or injection molding processes. While we do not provide primary casting or molding services, our expertise ensures cast or molded components meet stringent dimensional and surface finish requirements for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. Our facility bridges the gap between near-net-shape manufacturing and final part certification through precision subtractive techniques.
Our core capability centers on 5-axis CNC machining centers, including DMG MORI CTX beta 1250 and Makino D200Z systems. These platforms enable complex geometry processing in a single setup, eliminating cumulative errors from multiple fixtures. We machine aluminum alloys (e.g., 7075-T6), stainless steels (17-4PH, 316L), titanium (Grade 5), and high-temperature superalloys (Inconel 718) with material removal rates optimized for minimal thermal distortion. Integrated probing systems perform in-process verification, ensuring feature alignment within 0.010 mm before final inspection.
Quality control is executed through a tiered inspection protocol. All critical dimensions undergo verification via Zeiss CONTURA and Hexagon GLOBAL S 121510 CMMs, programmed to ISO 10360-2 standards. First-article inspections follow AS9102 formats for aerospace clients, while medical device batches include full PPAP documentation with SPC data. Surface roughness is validated using Mitutoyo SJ-410 profilometers, with typical finishes achieving Ra 0.4 µm on milled surfaces and Ra 0.2 µm on ground features.
Tolerance performance is rigorously maintained across production runs. The table below defines achievable limits based on material and feature complexity under controlled environmental conditions (20±1°C):
| Material Type | Standard Tolerance (mm) | Precision Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | ±0.05 | ±0.005 |
| Stainless Steels | ±0.03 | ±0.008 |
| Titanium Alloys | ±0.04 | ±0.010 |
| Nickel Superalloys | ±0.05 | ±0.012 |
These tolerances exceed ISO 2768-mK benchmarks and are validated through Gage R&R studies with Cgk > 1.67. We maintain NIST-traceable calibration for all measurement equipment, with inspection reports including 3D deviation maps for critical datums. Our process control system monitors tool wear in real-time using spindle load analytics, triggering automatic tool compensation to sustain tolerance bands over 500+ part runs.
For components originating from casting or molding processes, we address inherent challenges such as porosity exposure during machining through adaptive cutting strategies and non-destructive verification. This integrated approach ensures final parts comply with ASME Y14.5 geometric dimensioning standards while maximizing yield from near-net-shape substrates. Wuxi Lead delivers certified precision where primary forming processes reach their functional limits.
Material & Finish Options
Material Selection in Casting vs Injection Molding: A Precision Engineering Guide
When determining the optimal manufacturing process for custom metal components, material selection plays a decisive role in performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in high-precision casting and metal injection molding (MIM), each suited to different material profiles and application demands. Understanding how aluminum, steel, and titanium behave in these processes ensures optimal part functionality across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Aluminum is widely favored in both die casting and high-pressure injection molding due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It is particularly effective in casting applications where complex geometries and lightweight structures are required. Aluminum alloys such as A380 and 6061 offer good machinability and are ideal for housings, heat sinks, and structural components. In metal injection molding, aluminum is less common due to challenges in sintering density, but advanced techniques are expanding its viability for small, intricate parts.
Steel, particularly stainless and tool steels, excels in metal injection molding where high strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability are critical. MIM processes allow for the production of small, complex steel components—such as surgical instruments or automotive sensors—with minimal post-processing. In casting, steel is typically used in investment or sand casting for larger, heavy-duty parts like valves and pump housings. While cast steel offers robust mechanical properties, it is generally heavier and more expensive to machine than aluminum.
Titanium stands out for its exceptional strength-to-density ratio and resistance to extreme environments, making it indispensable in aerospace and biomedical applications. Due to its high reactivity at elevated temperatures, titanium is rarely used in conventional casting and is more commonly processed via vacuum-based MIM or precision forging. Although costly, titanium’s performance in corrosive or high-stress environments justifies its use where reliability is non-negotiable.
Surface finishing further enhances material performance. Anodizing, primarily applied to aluminum, increases surface hardness, improves corrosion resistance, and allows for color coding. The anodized layer is integral to the base material, ensuring durability unmatched by paint or plating. While anodizing is not applicable to steel or titanium in the same way, these materials benefit from alternatives such as passivation, PVD coatings, or electropolishing.
Below is a comparative overview of key material properties and process compatibility:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Common Processes | Typical Finishes | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 2.7 | 310 | Die Casting, MIM | Anodizing, Powder Coating | Automotive, Electronics |
| Steel | 7.8 | 500–1200 | MIM, Investment Casting | Passivation, Plating | Medical, Industrial Tools |
| Titanium | 4.5 | 900–1100 | MIM, Forging | Anodizing (Type II/III), PVD | Aerospace, Implants |
Selecting the right material and process requires balancing design intent, environmental exposure, and production volume. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, our engineering team supports clients in optimizing this decision with data-driven material analysis and prototyping services.
Manufacturing Process & QC
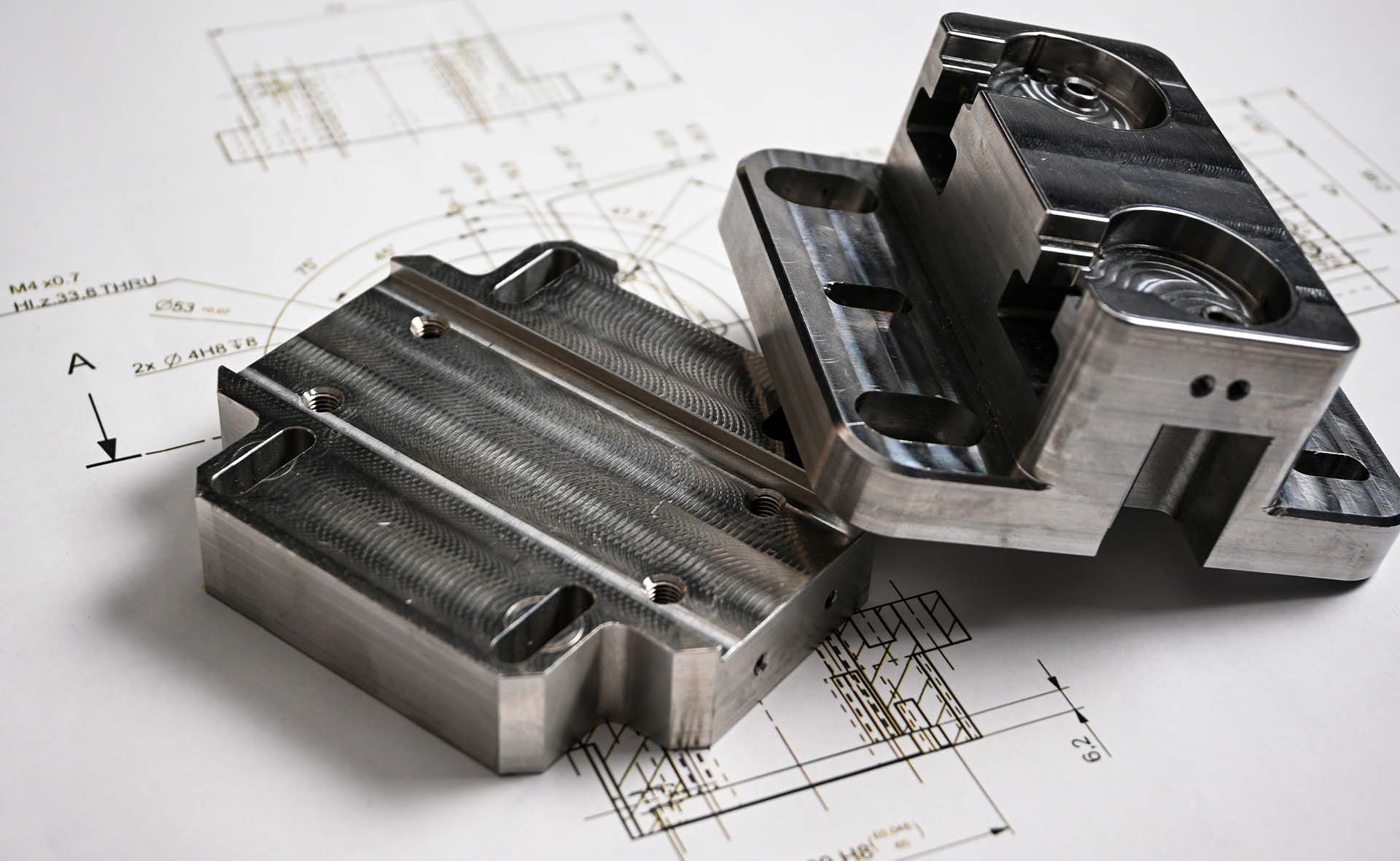

Strategic Process Integration for Zero-Defect Metal Manufacturing
Selecting between casting and injection molding demands rigorous alignment with design intent, material science, and production scalability. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we execute a seamless Design → Prototyping → Mass Production workflow to eliminate defects before volume manufacturing begins. This integrated approach ensures dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and cost efficiency for mission-critical components.
The design phase leverages advanced simulation software to model thermal dynamics, flow behavior, and stress distribution. For casting—whether sand, investment, or die casting—designers prioritize gating systems and solidification rates to prevent porosity. Injection molding (including metal injection molding, MIM) requires meticulous attention to wall thickness uniformity and ejection mechanics to avoid sink marks or warpage. Concurrent engineering with our clients validates manufacturability early, reducing downstream rework. Prototyping follows with rapid tooling: sand casting enables low-cost metal prototypes in 10–15 days, while MIM uses soft tooling for polymer-bonded prototypes in 7–10 days. Each prototype undergoes CMM inspection and metallurgical analysis to verify conformance to ISO 2768-mK tolerances and material specifications.
Mass production transitions only after prototype validation. Casting employs automated pouring systems and real-time X-ray monitoring to control microstructure. MIM utilizes multi-cavity molds with in-mold sensors for cavity pressure and temperature, ensuring ±0.3% dimensional repeatability. Both processes integrate statistical process control (SPC) with 100% automated optical inspection (AOI) for surface defects. Crucially, our zero-defect mandate hinges on traceability: every component’s thermal history, pressure curve, and inspection data are logged via IoT-enabled machinery for full production forensics.
Key technical differentiators between processes are summarized below:
| Parameter | Casting (High-Pressure Die) | Metal Injection Molding (MIM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Range | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium | Stainless Steel, Tool Steels |
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.1 mm | ±0.05 mm |
| Lead Time (10k pcs) | 25–35 days | 18–28 days |
| Min. Wall Thickness | 1.5 mm | 0.5 mm |
| Secondary Operations | Machining, Heat Treatment | Sintering, Precision Machining |
| Best For | Large structural parts (>1 kg) | Complex miniaturized parts (<100g) |
Zero defects emerge from synchronizing these phases, not isolated excellence. Our clients achieve 99.98% first-pass yield by treating design as a manufacturing constraint, prototyping as a validation checkpoint, and mass production as a closed-loop system. Wuxi Lead’s engineering team partners with you to select the optimal process—ensuring your component’s performance, cost, and reliability targets are met without compromise. This is precision manufacturing engineered for certainty.
Why Choose Wuxi Lead Precision
When evaluating casting versus injection molding for your next high-volume, precision-driven manufacturing project, the decision extends beyond material and geometry—it hinges on partnership, precision, and long-term reliability. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in custom metal manufacturing solutions that bridge the gap between traditional casting efficiency and the tight tolerances demanded by modern engineering applications. Our expertise isn’t limited to execution—we guide you through the selection process, ensuring your production method aligns with performance requirements, cost targets, and scalability goals.
Casting offers exceptional versatility for large, complex metal components, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and heavy industrial sectors. It supports a wide range of alloys and enables near-net-shape production, minimizing waste. Injection molding, while typically associated with plastics, has advanced metal variants such as metal injection molding (MIM), ideal for small, intricate parts requiring high volume and micron-level accuracy. However, the choice between these methods demands technical insight—material behavior, tooling longevity, surface finish requirements, and post-processing needs all influence the optimal path.
At Lead Precision, we combine deep metallurgical knowledge with advanced CNC finishing and quality control systems to deliver components that meet ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 standards. Whether you require investment casting for turbine blades or MIM for medical device housings, our engineering team collaborates with yours from design validation through full-scale production. We operate state-of-the-art facilities equipped with 5-axis machining centers, vacuum furnaces, and coordinate measuring machines, ensuring every part meets your exact specifications.
Our clients choose us not only for our technical capabilities but for our commitment to transparency, responsiveness, and continuous improvement. We understand that downtime is costly, which is why we maintain rigorous lead time control and offer real-time production tracking. From prototype to serial production, we adapt to your supply chain rhythms, supporting just-in-time delivery without compromising quality.
Below is a comparison of key performance parameters across common casting and metal injection molding processes:
| Parameter | Investment Casting | Die Casting | Metal Injection Molding (MIM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Materials | Stainless Steel, Ti, Ni Alloys | Al, Zn, Mg Alloys | Stainless Steel, Low-Alloy Steels |
| Tolerance Range | ±0.076 mm | ±0.10 mm | ±0.05 mm |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | 1.6 – 3.2 µm | 0.8 – 2.0 µm | 0.8 – 1.6 µm |
| Part Size Range | 10 g – 100 kg | 50 g – 20 kg | 0.1 g – 250 g |
| Production Volume | Low to Medium | High | Very High |
| Tooling Cost | Moderate | High | High |
| Secondary Operations | Machining, Heat Treat | Minimal | Sintering, Optional Machining |
Partner with Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery to make an informed, strategic decision between casting and injection molding—backed by engineering rigor and manufacturing excellence. Contact us today at [email protected] to discuss your project requirements, request a DFM analysis, or receive a competitive quote. Let us be your precision manufacturing ally in China.
⚙️ Precision Cost Estimator
Estimate relative manufacturing effort based on tolerance.

