Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Insert Mold Vs Overmold
Engineering Insight: Insert Mold vs Overmold – The Precision Imperative in High-End Manufacturing
In the realm of advanced metal manufacturing, the distinction between insert molding and overmolding is more than a technical nuance—it is a critical decision point that defines product performance, durability, and manufacturing efficiency. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we understand that precision is not an optional attribute but a foundational requirement, especially when serving industries where failure is not an option. Our experience delivering components for Olympic-grade equipment and military-grade systems underscores our commitment to dimensional accuracy, material integrity, and process reliability.
Insert molding involves placing a pre-formed metal component—often CNC-machined with micron-level tolerances—into a mold cavity before injecting molten polymer around it. This technique creates a permanent mechanical bond, ideal for applications requiring high structural integrity, such as sensor housings or electrical connectors. The success of insert molding hinges on the precision of the metal insert. Even minor deviations in geometry or surface finish can lead to misalignment, weak bonding, or functional failure under stress.
Overmolding, by contrast, typically involves molding a secondary polymer layer over an existing substrate—often another polymer or a metal part—to enhance ergonomics, sealing, or electrical insulation. While the process appears similar, overmolding demands precise control over material adhesion, thermal expansion, and layer thickness. In high-performance environments, such as aerospace or defense systems, the interfacial strength between layers must withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, and mechanical shock. This requires not only advanced tooling but also deep material science expertise.
At Lead Precision, our CNC-machined metal components are engineered to serve as the core structural element in both insert and overmolded assemblies. We utilize multi-axis machining centers with sub-micron repeatability, ensuring that every insert meets exacting dimensional and surface specifications. Our quality control protocols include coordinate measuring machine (CMM) verification, optical inspection, and adhesion testing under simulated operational conditions.
The choice between insert molding and overmolding should be guided by functional requirements, but the success of either process depends on the precision of the metal component. Whether supporting Olympic athletes with lightweight, high-strength assemblies or equipping military systems with corrosion-resistant, thermally stable housings, Lead Precision delivers metal parts that form the backbone of reliable, high-performance products.
| Specification | Insert Molding | Overmolding |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Tolerance (Metal Component) | ±0.005 mm | ±0.01 mm |
| Bonding Mechanism | Mechanical interlock | Adhesive/thermal fusion |
| Common Applications | Electrical connectors, sensor housings | Grips, sealed enclosures |
| Material Compatibility | Metal + Thermoplastics | Polymer + Polymer, Metal + Elastomer |
| Key Challenge | Insert alignment and thermal stability | Interlayer adhesion, warpage control |
| Lead Precision Capability | CNC-turned inserts with surface treatments | Precision-machined substrates for overmold adhesion |
Precision is not a final step—it is engineered into every phase of production. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we ensure that whether your design calls for insert molding or overmolding, the metal foundation is flawless.
Precision Specs & Tolerances
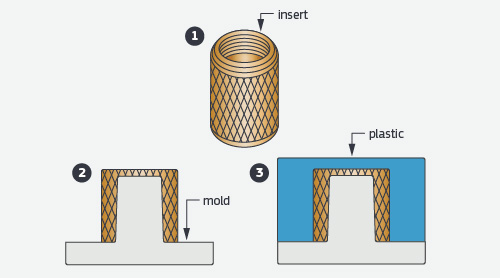
Technical Capabilities: Precision Metal Components for Insert Molding and Overmolding Applications
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in manufacturing the critical metal components that form the foundation of high-integrity insert molding and overmolding assemblies. Insert molding integrates pre-formed metal parts directly into a plastic matrix during the injection process, creating a single robust component where the metal provides structural strength, conductivity, or mounting points. Overmolding involves adding a secondary layer of material, typically elastomeric or plastic, over an existing substrate—often a metal part we produce—to enhance grip, sealing, aesthetics, or electrical insulation. Our core expertise lies in producing the complex, high-precision metal inserts, frames, pins, and housings demanded by these advanced processes, ensuring perfect integration and long-term reliability in demanding end-use environments.
Our advanced manufacturing capabilities are centered around state-of-the-art 5-axis CNC machining centers. This technology enables us to produce geometrically intricate metal components with exceptional accuracy and surface finish, essential for seamless molding integration. Multi-axis simultaneous machining eliminates the need for multiple setups, drastically reducing cumulative error and ensuring critical features maintain precise positional relationships. We routinely machine complex contours, deep cavities, undercuts, and fine details in a wide range of engineering metals including stainless steel, aluminum alloys, brass, and specialty alloys, meeting the exacting thermal and mechanical requirements of subsequent molding cycles.
Achieving the tight tolerances demanded by modern insert and overmolding applications requires rigorous process control and verification. Every component undergoes comprehensive dimensional inspection using calibrated Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM). Our CMM protocols validate critical dimensions, geometric tolerances (GD&T), and surface profiles against the original engineering specifications, providing documented evidence of conformance. This systematic QC approach guarantees that metal parts arrive at the molding facility ready for production, minimizing scrap, reducing cycle times, and ensuring consistent final product quality. Our engineering team collaborates closely with clients during the design phase to optimize part geometry for both machinability and successful molding integration.
The following table outlines our standard achievable machining tolerances for critical features on metal components destined for insert molding and overmolding applications. These capabilities represent typical production performance under controlled conditions; tighter tolerances are achievable for specific features upon engineering review.
| Feature Type | Standard Tolerance | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions | ±0.005 mm | Up to 50 mm; ±0.01 mm typical for 50-150 mm |
| Angular Dimensions | ±0.05° | Verified via CMM |
| Positional Tolerance | ±0.01 mm | Relative to primary datums (per ISO 2768) |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.4 – 0.8 µm | Standard machined finish; finer available |
| Concentricity | 0.01 mm | Critical for pins/shafts |
Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery delivers the dimensional integrity and surface quality required for successful high-volume insert molding and overmolding. Our 5-axis CNC expertise combined with stringent CMM-based quality assurance ensures your metal substrates perform flawlessly within the molding process, directly contributing to the durability and functionality of the final assembled product. Contact our engineering team to discuss optimizing your metal component design for molding integration.
Material & Finish Options
Material Selection for Insert Molding and Overmolding Applications
In high-precision insert molding and overmolding processes, material selection is critical to achieving optimal performance, durability, and compatibility between the metal component and the overmolded polymer. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in custom metal manufacturing using aluminum, steel, and titanium—each offering distinct mechanical and thermal properties suited to specific industrial applications. Understanding these materials and their surface treatments, such as anodizing, ensures long-term reliability in demanding environments.
Aluminum is widely used in insert molding due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, thermal conductivity, and machinability. It is particularly suitable for applications requiring lightweight components with efficient heat dissipation, such as in automotive sensors or consumer electronics. When paired with thermoplastic overmolding materials like PBT or nylon, aluminum provides structural integrity while enabling design flexibility. Anodizing aluminum enhances its surface hardness and corrosion resistance, creating a porous oxide layer that also improves adhesion with the overmolded material. Type II (sulfuric acid) and Type III (hardcoat) anodizing are commonly applied, with Type III offering superior wear resistance for industrial-grade components.
Steel, particularly stainless and tool grades, is selected when maximum strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability are required. It is ideal for high-cycle molding tools or inserts subjected to mechanical stress. While heavier than aluminum, steel maintains its integrity under elevated temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure. Surface treatments such as passivation or electroless nickel plating are often used to improve corrosion resistance and bonding performance. However, unlike aluminum, steel does not benefit from anodizing and requires alternative finishing methods to optimize polymer adhesion.
Titanium offers the highest strength-to-density ratio among the three materials and exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in saline or chemically aggressive environments. Its use in overmolding is less common due to higher cost and machining complexity, but it is indispensable in aerospace, medical, and marine applications where performance outweighs cost considerations. Titanium can be anodized to modify surface energy and improve bonding, although the process differs from aluminum anodizing and requires precise control of voltage and electrolyte.
Below is a comparative overview of key material properties relevant to insert and overmolding applications.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Common Finishes | Bonding Readiness with Polymers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.7 | 310 | 167 | Anodizing (Type II/III) | High (with anodizing) |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 8.0 | 505 | 16 | Passivation, Nickel Plating | Moderate (requires surface prep) |
| Titanium Grade 5 | 4.4 | 895 | 6.7 | Anodizing, Abrasive Prep | Moderate to High |
Selecting the appropriate material and finish directly impacts the success of the overmolding process, influencing adhesion, thermal cycling performance, and long-term reliability. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we support clients in matching material properties with application demands, ensuring precision-engineered solutions for advanced manufacturing challenges.
Manufacturing Process & QC
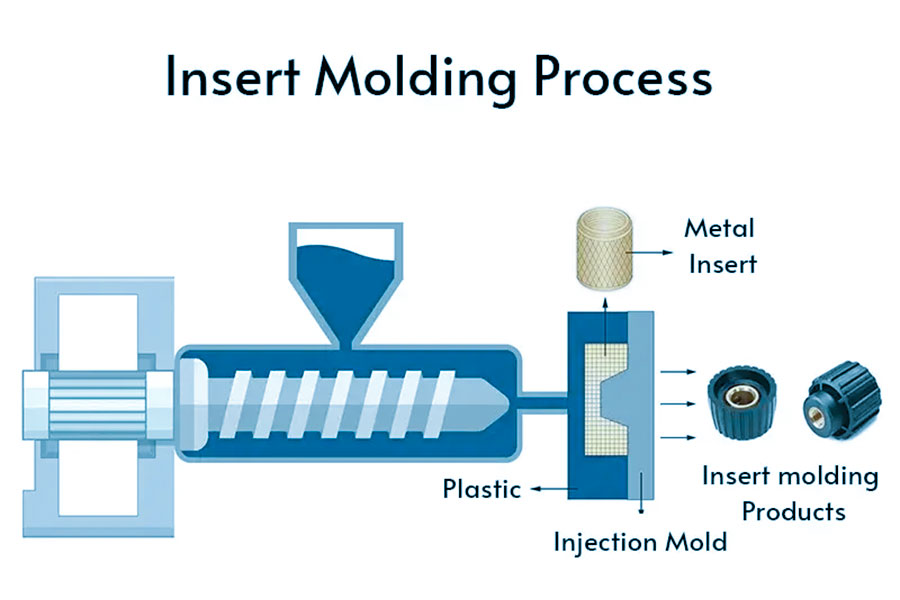
Insert Molding vs Overmolding: Precision Execution from Design to Zero-Defect Production
Selecting between insert molding and overmolding demands rigorous process alignment with functional requirements. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we initiate with collaborative design engineering to eliminate downstream defects. For insert molding, metal substrate geometry and surface treatment—such as micro-roughening or plasma coating—are optimized for mechanical interlock with the polymer. Overmolding requires precise analysis of material adhesion chemistry, ensuring elastomer compatibility with the base substrate through rigorous bond-strength simulations. Both processes mandate mold flow analysis to predict knit lines, sink marks, and residual stress, validated via 3D-printed prototypes for form, fit, and initial function testing.
Prototyping transitions into production only after thermal aging and dimensional validation under ISO 2768 tolerances. Insert molding prototypes undergo torque testing to verify substrate retention, while overmolded units endure peel tests to confirm interfacial integrity. Our facility employs in-mold sensors during prototyping to capture real-time pressure and temperature data, feeding corrections into the mass production process. This phase ensures zero defects by identifying micro-shrinkage or warpage risks before tooling finalization.
Mass production leverages closed-loop control systems for consistent outcomes. Insert molding utilizes robotic loaders for substrate placement accuracy within ±0.02mm, paired with cavity pressure monitoring to detect bonding anomalies. Overmolding employs sequential injection sequencing with sub-10-millisecond timing control to prevent material wash-off. Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts track critical dimensions hourly, with automated vision systems rejecting non-conforming parts at 100% inspection rates. Tool maintenance follows predictive schedules based on shot counters and thermal imaging, preventing wear-induced deviations.
The following specifications highlight key process differentiators for informed decision-making:
| Parameter | Insert Molding | Overmolding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Metals + Thermoplastics | Plastics + Elastomers/TPU |
| Tolerance Capability | ±0.005mm (substrate) | ±0.05mm (bond line) |
| Production Speed | 30-60 seconds/cycle | 45-90 seconds/cycle |
| Critical Control Point | Substrate positioning accuracy | Material adhesion temperature |
Wuxi Lead’s zero-defect mandate is enforced through end-of-line testing: insert-molded components undergo pull-force validation per ASTM D638, while overmolded assemblies endure 500-cycle flex testing. All data integrates into our digital twin platform, enabling traceability from raw material lot to finished part. This closed-loop methodology—grounded in precision engineering and proactive defect prevention—ensures your high-complexity components meet aerospace, medical, and automotive reliability standards without compromise. Partner with us to transform design intent into flawless production reality.
Why Choose Wuxi Lead Precision
Choosing the right manufacturing process for your precision components is not just about cost or speed—it’s about long-term reliability, performance, and total product lifecycle value. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in high-end custom metal manufacturing with deep expertise in insert molding and overmolding technologies. Whether your application demands the structural integrity of metal inserts encapsulated in polymer or a seamless dual-material design for enhanced ergonomics and sealing, our engineering team delivers solutions that meet exacting industrial standards.
Insert molding and overmolding are often confused, yet they serve distinct purposes. Insert molding involves placing a pre-formed metal component—typically machined with extreme precision—into a mold cavity before injecting plastic around it. This creates a permanent bond where the metal provides strength, conductivity, or mounting functionality. Overmolding, by contrast, typically involves molding a second material—often a soft-touch thermoplastic elastomer—over an existing substrate, which may be plastic or metal, to improve grip, sealing, or user interface.
The decision between these processes hinges on your product’s mechanical, thermal, and environmental requirements. At Lead Precision, we don’t just manufacture parts—we engineer solutions. Our in-house capabilities span CNC machining, insert preparation, mold design, and multi-shot molding, allowing us to control quality at every stage. We work closely with clients to evaluate load-bearing needs, chemical exposure, temperature ranges, and assembly methods to determine the optimal approach.
Our clients span industries where failure is not an option—automotive sensors, medical devices, industrial automation, and high-reliability consumer electronics. We adhere to ISO 13485, IATF 16949, and ISO 9001 standards, ensuring every component meets global compliance benchmarks. With advanced simulation tools and DFM analysis, we reduce risk and accelerate time to market.
Below is a comparison of key technical parameters we evaluate during process selection:
| Parameter | Insert Molding | Overmolding |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Metal (stainless steel, brass, etc.) | Plastic or metal |
| Bond Strength | High (mechanical interlock) | Medium to High (adhesive/thermal) |
| Typical Applications | Connectors, sensors, threaded parts | Grips, seals, ergonomic surfaces |
| Tooling Complexity | Moderate to High | High (multi-cavity, sequential) |
| Tolerance Control | ±0.02 mm (with precision inserts) | ±0.05 mm (dependent on substrate) |
| Production Efficiency | High (single-shot integration) | Moderate (multi-step process) |
| Secondary Operations | Minimal | May require priming or pre-treatment |
Partnering with Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery means gaining a true engineering collaborator. We don’t just follow drawings—we challenge assumptions, optimize designs, and deliver manufacturable solutions that perform in real-world conditions. Our facility in Wuxi is equipped with 5-axis CNC centers, electric injection molding machines, and full metrology labs to support rapid prototyping and high-volume production.
For your next high-performance component, let us help you decide between insert molding and overmolding with confidence. Contact us today at [email protected] to speak with one of our application engineers.
⚙️ Precision Cost Estimator
Estimate relative manufacturing effort based on tolerance.

