Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: 3D Printed Molds For Injection Molding
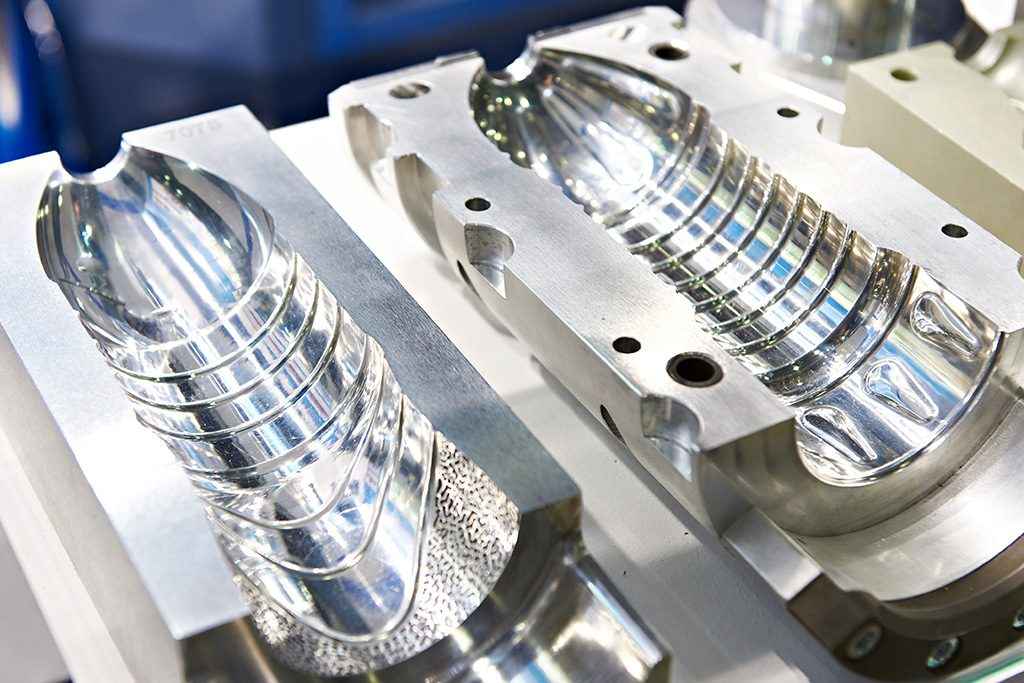

Engineering Insight: 3D Printed Molds for Injection Molding
In the evolving landscape of custom metal manufacturing, 3D printed molds for injection molding have emerged as a transformative solution, blending rapid prototyping with functional production capabilities. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we recognize that the true value of additive manufacturing in mold fabrication lies not just in speed, but in precision. The integration of 3D printing into mold development demands exacting control over dimensional accuracy, thermal performance, and surface integrity—factors that directly influence part quality, cycle time, and tool longevity.
Precision in 3D printed molds begins with advanced design optimization. Unlike traditional subtractive methods, additive manufacturing allows for complex internal geometries such as conformal cooling channels, which significantly improve thermal regulation during injection cycles. However, the benefits of such features are only fully realized when the printing process maintains tight tolerances—typically within ±0.05 mm—and ensures consistent material density. At Lead Precision, our engineering team leverages industrial-grade metal 3D printing systems and rigorous post-processing protocols to achieve these standards, ensuring that each mold performs reliably under high-pressure, high-temperature conditions.
Our expertise in precision manufacturing has been validated through mission-critical applications. As a supplier of components used in Olympic-grade equipment and defense-related systems, we adhere to the highest standards of quality and repeatability. These projects demand zero-defect performance, where even micron-level deviations can compromise functionality. This same discipline is applied to our 3D printed molds, where we combine laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology with in-process monitoring and metrology-grade inspection to deliver molds that meet or exceed ISO 2768-mK geometric tolerances.
Beyond dimensional accuracy, material selection and post-build treatment are critical. We primarily use maraging steel (MS1) and tool steel (H13) powders, chosen for their excellent hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Each printed mold undergoes stress relief, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and precision CNC machining to achieve final dimensions and surface finish. This hybrid approach ensures structural integrity while maintaining the design flexibility that additive manufacturing offers.
The following table outlines key specifications for our 3D printed injection molds:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Printing Technology | Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) |
| Layer Thickness | 20–40 μm |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.05 mm |
| Surface Roughness (as-printed) | Ra 12–16 μm |
| Surface Roughness (post-processed) | Ra 0.8–1.6 μm |
| Materials | Maraging Steel (MS1), H13 Tool Steel |
| Max Build Volume | 250 × 250 × 300 mm |
| Support for Conformal Cooling | Full design and fabrication capability |
| Post-Processing | Stress relief, HIP, CNC finishing, polishing |
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we view 3D printed molds not as experimental tools, but as precision-engineered systems integral to advanced manufacturing. Our experience in high-stakes industries ensures that every mold we produce meets the uncompromising demands of performance, consistency, and quality.
Precision Specs & Tolerances
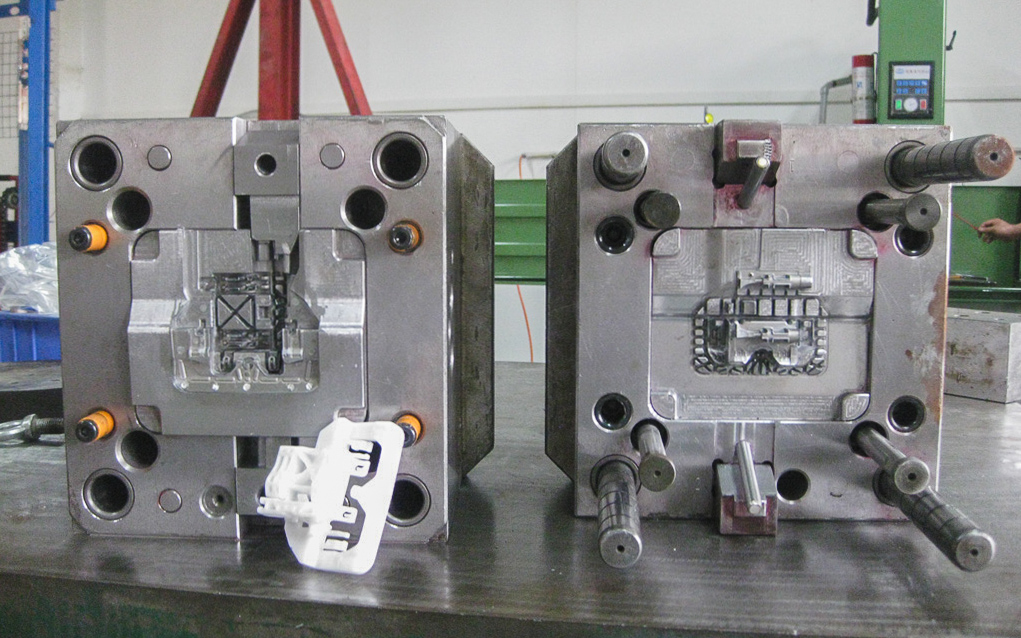
Technical Capabilities for 3D Printed Injection Molds
Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery delivers mission-critical metal manufacturing solutions for advanced 3D printed injection molds. Our expertise bridges additive manufacturing’s design freedom with the stringent demands of high-volume production. We specialize in post-processing printed mold cores, cavities, and inserts to achieve the dimensional stability, surface integrity, and thermal management required for commercial injection molding. This ensures printed molds withstand prolonged cycling without degradation in part quality or mold life.
Our 5-axis CNC machining center forms the backbone of this capability. Utilizing DMG MORI and Hermle platforms with integrated thermal compensation, we achieve micron-level precision on complex organic geometries inherent to printed molds. Simultaneous 5-axis motion allows single-setup machining of conformal cooling channels, undercuts, and micro-features that traditional methods cannot access. This eliminates cumulative errors from multiple fixtures and preserves the intricate topology optimized during the additive phase. All machining employs high-rigidity spindles (42,000 RPM) and diamond-coated tools to maintain surface finishes critical for part ejection and cosmetic quality. Material compatibility spans tool steels (H13, S136), aluminum alloys, and copper composites, with tailored cutting strategies for each substrate’s thermal and mechanical properties.
Quality assurance is non-negotiable. Every mold component undergoes comprehensive CMM inspection using Zeiss CONTURA systems with 0.5μm volumetric accuracy. We validate critical dimensions against CAD models, including cooling channel alignment, parting line flatness, and cavity radii. This process captures thermal distortion effects by simulating operational temperatures during measurement. Statistical process control (SPC) tracks capability indices (Cp/Cpk) for recurring features, ensuring tolerance stack-up remains within client specifications across production runs. Our inspection regime extends beyond dimensional checks to include surface roughness profiling (per ISO 4287) and hardness verification at critical wear points.
The table below details achievable tolerances for printed mold components after our precision finishing process:
| Feature Category | Specification | Measurement Method | Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Axes | ±0.003 mm | CMM | Zeiss CONTURA |
| Positional Accuracy | ±0.005 mm | Laser Interferometer | Renishaw XL-80 |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.4 μm (cavities) | Profilometer | Mitutoyo SJ-410 |
| Parting Line Flatness | 0.008 mm over 100mm | Optical Comparator | Nikon MM-40 |
| Cooling Channel Alignment | ±0.01 mm | CMM with probe extension | Zeiss CONTURA |
This technical rigor transforms 3D printed molds from prototyping tools into production assets. By controlling thermal gradients through precision-machined conformal cooling and validating every micron of geometry, Wuxi Lead ensures your printed molds deliver consistent part quality, reduced cycle times, and extended service life. We partner with clients from design validation through first-article inspection, providing full traceability and actionable data to optimize your injection molding process. Contact our engineering team to discuss tolerance requirements for your specific application.
Material & Finish Options
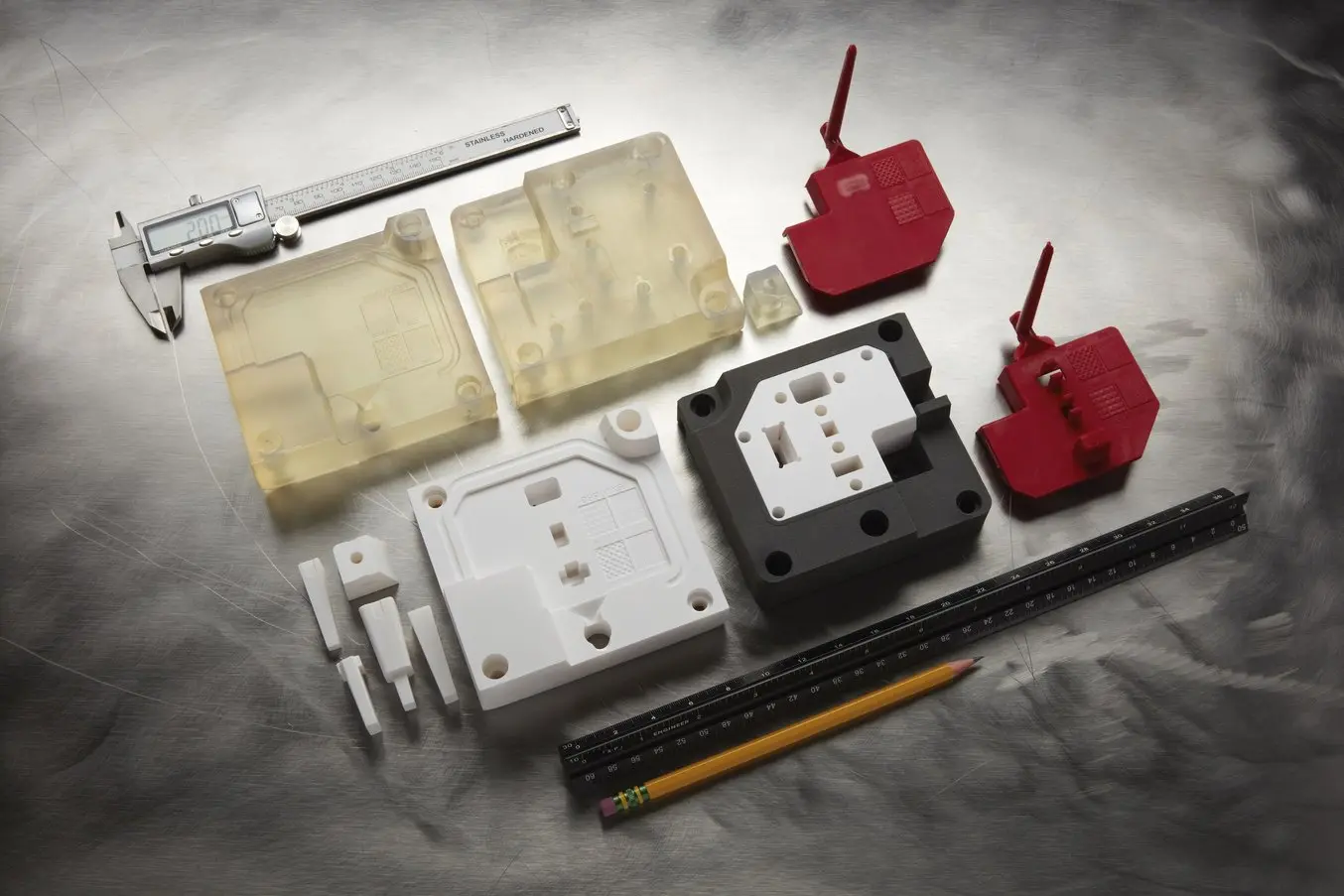
When designing 3D printed molds for injection molding, material selection is a critical determinant of mold performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in custom metal manufacturing solutions that leverage advanced 3D printing technologies to produce high-precision molds tailored to specific production requirements. The primary materials used in this process—aluminum, steel, and titanium—each offer distinct advantages depending on application demands such as cycle volume, part complexity, thermal management, and environmental resistance.
Aluminum is widely favored for prototyping and low-to-medium volume production due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and ease of machining. It enables rapid heat dissipation, reducing cycle times and improving efficiency during injection processes. While not as hard-wearing as steel, modern aluminum alloys suitable for additive manufacturing exhibit sufficient durability for thousands of cycles when properly treated. It is an optimal choice for molds requiring fast turnaround and iterative design validation.
Steel, particularly tool steels like H13 or P20, delivers superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. This makes it ideal for high-volume production runs where mold longevity is paramount. 3D printed steel molds can withstand repeated thermal cycling and aggressive polymers without significant degradation. Although steel has lower thermal conductivity than aluminum, strategic conformal cooling channel design made possible through additive manufacturing compensates by enhancing cooling efficiency within the mold body.
Titanium, while less common in standard mold applications, offers exceptional strength-to-density ratio and corrosion resistance. Its use is typically reserved for specialized environments involving highly corrosive materials or where extreme durability in a lightweight package is required. Titanium’s biocompatibility also makes it suitable for medical-grade plastic components. However, due to higher material and processing costs, its application remains niche.
Surface finish plays a crucial role in part quality and mold maintenance. Anodizing is a commonly specified post-processing treatment, especially for aluminum molds. It increases surface hardness, improves wear resistance, and enhances corrosion protection. Type II (sulfuric acid) anodizing provides a decorative and moderately durable finish, while Type III (hard anodizing) delivers a thick, engineered coating capable of withstanding industrial use. Other finishes such as polishing, bead blasting, or PVD coatings may be applied based on aesthetic or functional requirements.
The following table outlines key mechanical and thermal properties of the three primary materials used in 3D printed molds:
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HRC) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (AlSi10Mg) | 400–500 | 80–95 HB | 120–150 | Prototyping, low-volume production |
| Steel (H13) | 1800–2000 | 48–52 | 30–35 | High-volume production |
| Titanium (Ti6Al4V) | 900–1000 | 36–40 | 6–7 | Corrosive environments, medical |
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we guide clients through material and finish selection based on production volume, polymer type, and part geometry, ensuring optimal performance and return on investment.
Manufacturing Process & QC
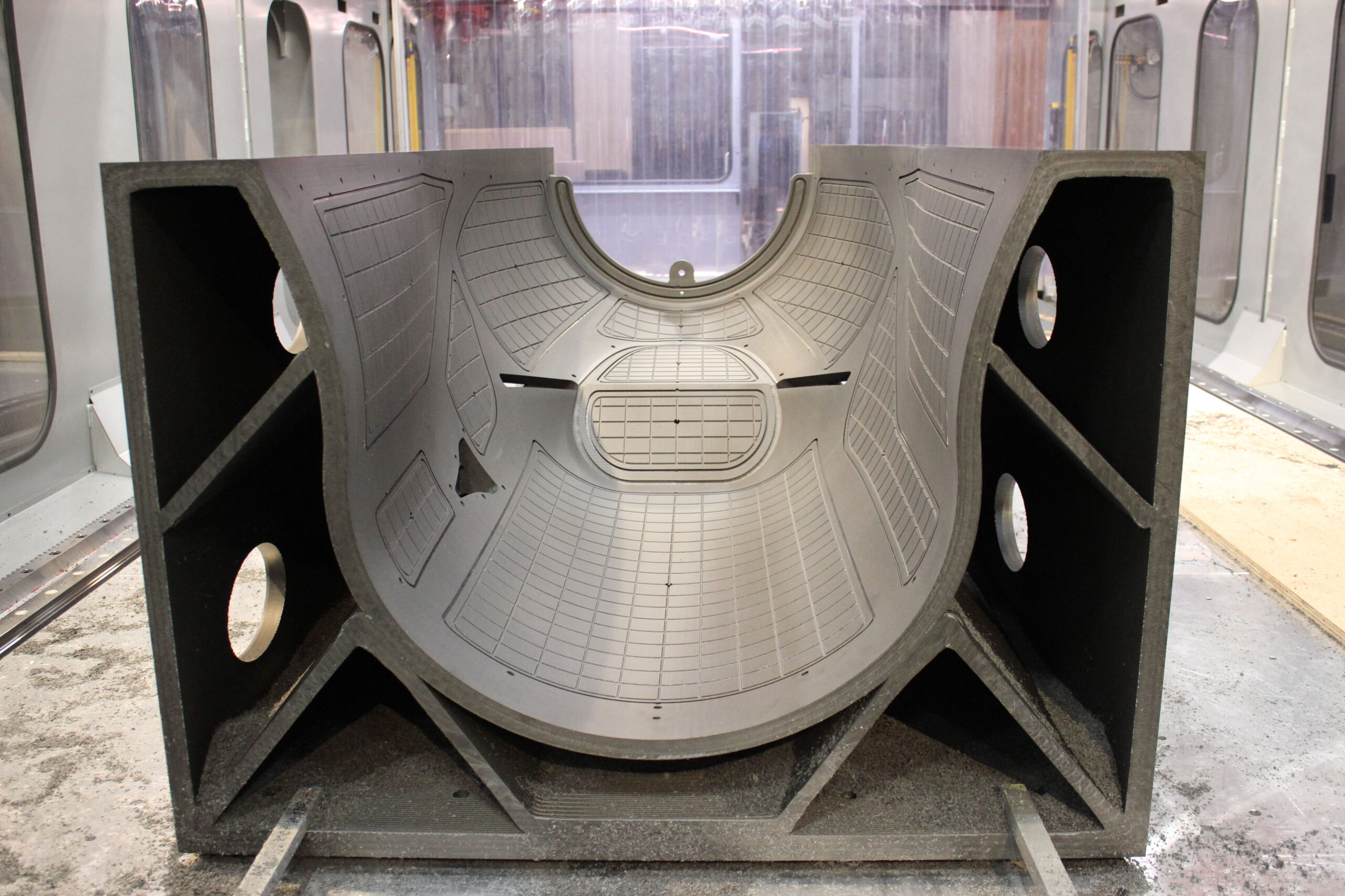
Production Process: Zero Defects Execution for 3D Printed Injection Molds
Achieving flawless injection molding with 3D printed tooling demands a rigorously controlled production sequence. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, our integrated workflow eliminates defects at every stage, transforming conceptual designs into high-volume production assets. This precision-engineered pathway ensures optimal part quality, reduced cycle times, and maximum tool longevity.
The process initiates with Advanced Design Engineering. Our engineers utilize high-fidelity simulation software to model thermal dynamics, material flow, and structural stress within the mold cavity. This virtual prototyping identifies potential warpage, sink marks, or filling imbalances before physical production begins. Critical factors like conformal cooling channel geometry, gate location, and ejection mechanics are optimized for the specific polymer and part geometry. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis is mandatory, ensuring the mold design aligns perfectly with both the 3D printing capabilities and the injection molding press parameters. This phase establishes the foundational blueprint for zero defects by preempting failure modes.
Precision Prototyping & Validation follows immediately. Utilizing metal additive manufacturing (primarily DMLS or SLM with tool steel alloys), we produce the initial mold core, cavity, and critical inserts. This stage is not merely about creating a physical object; it is a stringent validation checkpoint. The printed mold undergoes comprehensive metrology, including CMM inspection against the nominal CAD model to verify dimensional accuracy and surface finish. It is then mounted on a production-specification injection molding machine for rigorous functional testing. Short-run trials assess cooling efficiency, part ejection consistency, and initial surface replication. Any micro-defects in the molded parts trigger immediate, data-driven design iterations. Only molds consistently producing conforming parts under simulated production conditions advance to full-scale manufacturing.
Controlled Mass Production Deployment leverages the validated mold within a closed-loop monitoring system. Real-time sensors track cavity pressure, melt temperature, and cooling rates during every cycle, comparing data against the established golden parameters from the validation phase. Automated part inspection systems, often integrated vision or laser scanning, verify critical dimensions and surface integrity on a per-part or statistical basis. Any parameter deviation outside the stringent tolerance band triggers an immediate alert and process correction, preventing defect propagation. Our production environment maintains strict environmental controls and adheres to ISO 9001 protocols, ensuring process stability over extended runs. Continuous data logging enables predictive maintenance of the mold itself, preventing wear-related defects before they occur.
This phased approach, underpinned by advanced simulation, empirical validation, and real-time analytics, is non-negotiable for zero-defect outcomes. The following table details critical process specifications achievable through our methodology:
| Process Stage | Key Parameters | Tolerance Range | Typical Lead Time | Quality Control Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design Engineering | Simulation Fidelity, DFM Compliance | N/A (Virtual) | 5-10 Days | CAE Validation, Expert Review |
| Prototyping | Dimensional Accuracy, Surface Finish | ±0.025 mm, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm | 7-12 Days | CMM, Mold Trials, Part Metrology |
| Mass Production | Process Stability, Part Consistency | ±0.05 mm (part) | Continuous | Real-time Sensors, Automated Vision |
Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery guarantees this disciplined execution. We transform the potential of 3D printed molds into reliable, high-yield production reality, where zero defects is the engineered standard, not an aspiration.
Why Choose Wuxi Lead Precision
Partner with Lead Precision for Advanced 3D Printed Molds in Injection Molding
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in delivering high-performance, custom metal manufacturing solutions that meet the exacting demands of modern injection molding. As industry leaders in precision engineering and additive manufacturing, we offer a unique advantage in the production of 3D printed molds—combining rapid prototyping capabilities with industrial-grade durability. Our advanced metal 3D printing technology enables faster time-to-market, reduced material waste, and enhanced mold complexity that traditional machining methods cannot achieve.
When you partner with Lead Precision, you gain access to a team of engineers with deep expertise in mold design, thermal optimization, and material science. We work closely with clients to convert conceptual designs into fully functional, high-precision molds tailored for specific production environments. Whether you require conformal cooling channels, lightweight mold inserts, or complex geometries for undercuts and fine surface details, our 3D printing capabilities deliver unmatched flexibility and performance.
Our state-of-the-art facilities in Wuxi, China, are equipped with metal laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) systems that support a range of high-strength alloys, including tool steels and stainless steels optimized for injection molding applications. Every mold undergoes rigorous quality control, including dimensional inspection, porosity testing, and surface finish optimization, ensuring consistent performance under high-cycle production conditions.
We understand that reliability, lead time, and technical support are critical in manufacturing. That’s why we integrate seamless project management from design to delivery, offering real-time updates and engineering consultations throughout the process. Our goal is not just to manufacture molds—we aim to become your long-term manufacturing partner, helping you innovate faster and scale efficiently.
Below are the key technical specifications we support for 3D printed molds:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Printing Technology | Metal Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) |
| Build Envelope | Up to 500 x 500 x 400 mm |
| Layer Thickness | 20–50 µm |
| Material Options | 1.2709 (Maraging Steel), 1.2343, 316L, Inconel 718 |
| Surface Roughness (as-built) | Ra 10–15 µm (can be polished to Ra <0.4 µm) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.05 mm per 100 mm |
| Post-Processing | Stress relief, HIP, CNC machining, polishing, coating |
| Lead Time (Typical) | 10–20 days (varies by complexity) |
By leveraging 3D printed molds from Lead Precision, manufacturers can achieve up to 70% faster cooling cycles, reduced part warpage, and extended mold life—critical advantages in high-volume production. Our solutions are trusted by automotive, medical, and consumer electronics manufacturers who demand precision, repeatability, and innovation.
Take the next step in advancing your injection molding capabilities. Contact us today at [email protected] to discuss your project requirements and discover how Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery can support your manufacturing goals with cutting-edge 3D printed mold technology.
⚙️ Precision Cost Estimator
Estimate relative manufacturing effort based on tolerance.

