Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: 3D Print Brass

Engineering Insight: 3D Printing Brass with Precision at Scale
In the evolving landscape of advanced metal manufacturing, 3D printing brass has emerged as a transformative capability—merging the aesthetic and functional benefits of brass with the geometric freedom of additive manufacturing. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we recognize that the true value of 3D printed brass lies not just in its novelty, but in the precision, consistency, and reliability with which it is produced. Brass, with its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and acoustic properties, is widely used in aerospace, marine, musical instruments, and high-end decorative components. When produced through selective laser melting (SLM) or binder jetting processes, brass components can achieve complex internal geometries unattainable through traditional casting or machining—provided the process is tightly controlled.
Precision in 3D printed brass is non-negotiable. Dimensional accuracy, surface integrity, and material homogeneity directly impact performance, especially in mission-critical applications. At Lead Precision, our engineering protocols are built on decades of experience in high-tolerance metal fabrication, including components certified for Olympic-standard equipment and defense-grade systems. These applications demand micron-level tolerances, repeatable mechanical properties, and full traceability—benchmarks we apply rigorously to every brass additive project.
Our 3D printing workflows integrate real-time monitoring, post-process heat treatment, and precision CNC finishing to ensure that each brass component meets exacting specifications. We utilize advanced powder bed fusion systems calibrated to manage the thermal dynamics of copper-zinc alloys, minimizing porosity and warping. Every build undergoes rigorous in-process inspection, followed by post-build metrology using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical scanning. This end-to-end control ensures that parts not only meet design intent but also perform reliably under operational stress.
Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery brings a unique advantage to 3D printed brass: the fusion of industrial-scale additive capabilities with the quality standards of precision engineering. Whether producing intricate fluid manifolds, custom actuators, or heritage restoration components, our process ensures repeatability across single prototypes and batch production.
The following table outlines key technical specifications for our 3D printed brass manufacturing capabilities.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material | CuZn15 (C26800), CuZn30 (C27200) |
| Build Volume | Up to 250 x 250 x 300 mm |
| Layer Thickness | 20–50 µm |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.05 mm (standard), ±0.02 mm (tight-tolerance) |
| Surface Roughness (as-printed) | Ra 8–12 µm |
| Post-Processing Options | CNC finishing, polishing, plating, HIP |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.3 mm |
| Lead Time (prototype) | 7–10 working days |
At Lead Precision, we treat every 3D printed brass component as a precision-engineered solution—not just an additively manufactured part. Our commitment to accuracy, backed by proven performance in elite industrial sectors, ensures that clients receive components that are as reliable as they are innovative.
Precision Specs & Tolerances

Precision Brass Manufacturing: Beyond Additive Limitations
While the phrase 3D print brass frequently appears in technical inquiries, Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery emphasizes that high-integrity brass components for aerospace, medical, and semiconductor applications demand subtractive precision. Brass poses significant challenges for metal additive processes including porosity, thermal distortion, and inconsistent mechanical properties. Our engineered solution leverages advanced 5-axis CNC milling and turning centers to deliver fully dense, isotropic brass parts meeting stringent industry performance criteria. This approach ensures optimal thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and machinability unattainable through current additive methods for critical applications.
Our HAAS and DMG MORI 5-axis platforms execute complex geometries in a single setup, eliminating cumulative alignment errors inherent in multi-operation workflows. Simultaneous 5-axis motion machines intricate contours, deep cavities, and undercuts in brass alloys including C36000, C26000, and C46400. High-speed spindles (24,000 RPM) paired with rigid tooling systems minimize chatter and burr formation—critical for brass’s tendency toward galling. In-process probing verifies workpiece alignment and compensates for thermal drift, while flood coolant management ensures dimensional stability during extended production runs.
Quality assurance is non-negotiable. Every brass component undergoes full-spectrum CMM inspection using Zeiss CONTURA systems with 0.00004″ (1 µm) volumetric accuracy. Automated reporting validates all critical dimensions against ASME Y14.5 standards, with surface roughness verified via Mitutoyo SJ-410 profilometers. Material certifications and heat traceability accompany each shipment, providing auditable compliance for regulated sectors.
The following table defines achievable tolerances for machined brass components under controlled production conditions
| Feature Type | Tolerance Range | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions | ±0.0002″ (±0.005 mm) | ISO 2768-mK |
| Angular Features | ±0.005° | ISO 2768-c |
| Positional Accuracy | ±0.0001″ (±0.0025 mm) | ISO 1101 |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 8–32 µin (0.2–0.8 µm) | ISO 1302 |
| Concentricity | 0.0004″ (0.01 mm) | ISO 1101 |
This capability framework enables clients to specify brass components with confidence for hydraulic manifolds, electrical connectors, and precision instrumentation where material integrity directly impacts system performance. By rejecting the limitations of additive brass processing, we deliver components with guaranteed mechanical properties, pressure tightness, and functional reliability. Partner with Wuxi Lead to transform brass design concepts into certified production assets—where micron-level precision meets industrial scalability.
Material & Finish Options
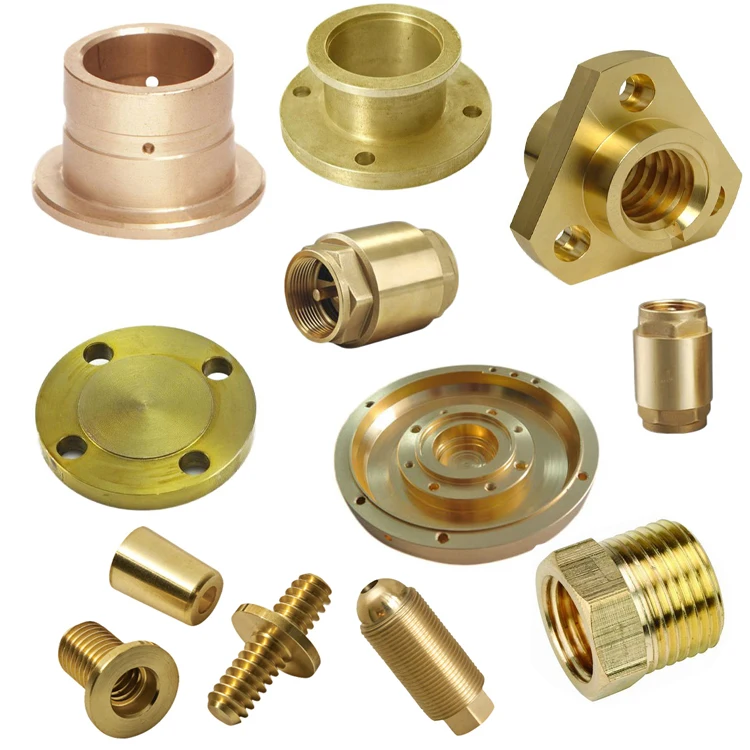

Material Selection for High-Performance 3D Printed Brass Components
When integrating 3D printed brass into advanced manufacturing workflows, understanding the interplay between base materials and surface treatments is critical. While brass itself serves as a versatile and aesthetically rich alloy, its performance in industrial applications can be significantly enhanced through strategic pairing with high-strength materials such as aluminum, steel, and titanium. These combinations are commonly used in hybrid assemblies where brass provides functional or decorative elements—such as threaded inserts, housings, or fluid connectors—while structural integrity is maintained by stronger substrates.
Aluminum remains a preferred choice for lightweight, high-conductivity applications. When mated with 3D printed brass components, it offers excellent thermal and electrical performance, making it ideal for aerospace electronics and automotive sensor housings. Its low density reduces overall system weight, though care must be taken to manage galvanic corrosion in humid or marine environments. Anodizing aluminum prior to integration provides a robust dielectric barrier, enhancing both corrosion resistance and wear performance.
Steel, particularly stainless variants such as 316L and 17-4 PH, delivers superior mechanical strength and environmental resilience. In systems requiring high pressure tolerance or long-term durability—such as hydraulic manifolds or industrial tooling—steel substrates paired with precision 3D printed brass fittings ensure reliable performance. The hardness of steel complements the machinability and ductility of brass, enabling tight-tolerance assemblies with minimal deformation under load.
Titanium stands at the pinnacle of performance materials, offering an exceptional strength-to-density ratio and outstanding resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive media. In mission-critical sectors like aerospace and medical implants, titanium structures with embedded or attached 3D printed brass elements combine biocompatibility, longevity, and design flexibility. Though more expensive and challenging to process, titanium’s long-term value in demanding environments justifies its use.
Surface finishing plays a decisive role in the functionality and lifespan of these hybrid systems. Anodizing, particularly Type II (sulfuric acid) and Type III (hardcoat), is widely applied to aluminum components to improve surface hardness and adhesion for sealing. While brass cannot be anodized in the traditional sense, it benefits from alternative surface treatments such as passivation, polishing, or lacquering to prevent oxidation and maintain luster. When designing multi-material assemblies, engineers must consider differential thermal expansion, electrochemical compatibility, and finishing sequence to ensure integrity across the entire component lifecycle.
The following table summarizes key material properties and compatibility considerations:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Common Use Cases | Anodizing Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.7 | 310 | Aerospace, Electronics | Yes (Type II & III) |
| Stainless Steel 316L | 8.0 | 580 | Marine, Medical | No |
| Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | 4.4 | 900 | Aerospace, Defense | Yes (non-protective color anodizing) |
| 3D Printed Brass (CuZn15) | 8.5 | 350 | Decorative, Fluid Systems | No (use passivation or lacquer) |
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we support comprehensive material integration strategies, ensuring that every 3D printed brass component meets the exacting standards of modern industrial design.
Manufacturing Process & QC
Precision Brass Additive Manufacturing Process: From Concept to Zero-Defect Production
At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, our 3D printing of brass components transcends conventional prototyping. We deliver mission-critical, production-ready parts through a rigorously controlled end-to-end process engineered for absolute dimensional fidelity and material integrity. Brass, particularly copper-zinc alloys, presents unique thermal and metallurgical challenges during additive manufacturing, including zinc vaporization risks and potential porosity. Our methodology systematically addresses these through integrated design validation, iterative prototyping, and closed-loop mass production controls, ensuring zero defects for demanding industrial applications.
The process commences with collaborative Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) engineering. Our specialists analyze your CAD model, optimizing geometry for brass powder bed fusion, incorporating strategic support structures to manage thermal distortion, and defining critical-to-quality (CTQ) features requiring post-process precision machining. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulates thermal stresses and predicts potential warpage, enabling proactive design adjustments before any material is consumed. This phase establishes the foundation for success, ensuring the digital model is inherently manufacturable to micron-level tolerances with brass.
Prototyping is not merely a validation step but a critical process refinement stage. We produce initial builds using your approved brass alloy, employing in-situ melt pool monitoring and layer-wise thermal imaging to detect anomalies in real-time. Each prototype undergoes comprehensive metrology: coordinate measuring machine (CMM) verification against nominal CAD data, micro-CT scanning for internal defect analysis, and mechanical property testing per ASTM standards. Feedback from this phase directly refines build parameters and post-processing sequences, guaranteeing the production recipe eliminates root causes of failure before scaling.
Mass production leverages our validated process within a controlled environment. Builds occur on calibrated industrial metal AM systems under inert atmosphere, with continuous monitoring of oxygen levels, laser power stability, and powder bed quality. Every layer is inspected optically; deviations trigger immediate corrective action. Post-build, parts undergo precision CNC machining for critical features, stress-relief heat treatment specific to the brass alloy, and non-destructive testing (NDT) such as penetrant or ultrasonic inspection. Final parts receive 100% dimensional inspection against your drawing, with full traceability of material lot, machine parameters, and inspection data. This closed-loop system, combining advanced AM with precision subtractive finishing, ensures consistent conformance to the most stringent aerospace, fluid power, and instrumentation specifications.
Key Brass Alloy Specifications for Additive Manufacturing
| Alloy Designation | Primary Composition | Typical Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Key Application Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C26000 (Cartridge Brass) | 70% Cu, 30% Zn | 8.50 – 8.80 | 350 – 450 | Excellent cold working, good corrosion resistance, standard for complex geometries |
| C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass) | 61.5% Cu, 35.5% Zn, 3.0% Pb | 8.45 – 8.65 | 400 – 500 | Superior machinability post-AM, ideal for components requiring tight-tolerance features after printing |
| C46400 (Naval Brass) | 59% Cu, 40% Zn, 1% Sn | 8.40 – 8.60 | 400 – 550 | Enhanced corrosion resistance in marine/saltwater environments, requires precise thermal management during build |
Wuxi Lead’s integrated approach transforms brass additive manufacturing from a prototyping tool into a reliable, high-precision production solution. By embedding zero-defect principles at every phase—from intelligent design through validated prototyping to tightly controlled mass production—we deliver brass components that perform flawlessly in your most critical assemblies, reducing your total cost of ownership through guaranteed quality and performance.
Why Choose Wuxi Lead Precision
When it comes to advanced metal manufacturing, particularly in the realm of 3D printed brass components, precision, material integrity, and engineering expertise are non-negotiable. At Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, we specialize in delivering high-performance, custom-manufactured brass parts using state-of-the-art additive manufacturing technologies. Our commitment to excellence positions us as the ideal partner for industries demanding complex geometries, tight tolerances, and superior surface finishes—without sacrificing structural integrity.
Partnering with Lead Precision means gaining access to a fully integrated manufacturing ecosystem. From initial design consultation to final quality inspection, our team of seasoned engineers and metallurgists ensures every 3D printed brass component meets exacting specifications. We utilize selective laser melting (SLM) and binder jetting techniques optimized for brass alloys, enabling us to produce intricate internal channels, lattice structures, and lightweight designs that traditional machining methods cannot achieve.
Our facility in Wuxi, China, is equipped with ISO-certified production lines and advanced post-processing capabilities, including hot isostatic pressing (HIP), precision CNC finishing, and surface treatments such as polishing and coating. This comprehensive approach guarantees not only dimensional accuracy but also enhanced mechanical properties and long-term durability in demanding operational environments.
We serve a global clientele across aerospace, medical devices, automotive R&D, and high-end industrial equipment, where reliability and repeatability are paramount. Whether you require rapid prototyping or low-volume production runs, our agile manufacturing model supports fast turnaround times without compromising quality.
Below are the key technical specifications for our 3D printed brass manufacturing process:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Options | CuZn15, CuZn30, Brass with Pb (on request), Custom Brass Alloys |
| Build Volume | Up to 250 x 250 x 300 mm (SLM), 400 x 250 x 200 mm (Binder Jet) |
| Layer Thickness | 20–50 μm |
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.05 mm |
| Surface Roughness (as-built) | Ra 8–12 μm (can be reduced to Ra 1–2 μm with polishing) |
| Density | > 99.5% (HIP treated) |
| Post-Processing Options | Stress relieving, annealing, CNC machining, polishing, plating |
| Quality Standards | ISO 9001:2015, Full traceability, First Article Inspection (FAI) reports |
Every project at Lead Precision is treated as a collaborative engineering effort. We work closely with your design and R&D teams to optimize part geometry for additive manufacturing, conduct thermal and stress simulations, and validate performance under real-world conditions. Our goal is not just to manufacture parts—but to co-develop solutions that push the boundaries of what’s possible with 3D printed brass.
For engineering teams seeking a reliable, technically proficient manufacturing partner, the next step is clear. Contact us today at [email protected] to discuss your project requirements, request material samples, or receive a detailed quote. Let Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery become your trusted partner in high-end metal additive manufacturing.
⚙️ Precision Cost Estimator
Estimate relative manufacturing effort based on tolerance.

